Duplicate data isn’t just annoying. It can be misleading, erroneous, or just plain wrong. Wrong information leads to wrong conclusions, and wrong conclusions lead to bad decisions.
So let’s clean up your worksheet by learning how to find, and then, how to remove duplicate entries in Excel.
What is a duplicate value?
Duplications may or may not be intentional. A duplicate value is simply one which is repeated throughout a dataset. Of course, duplicates are useful when we want to determine the frequency or number of occurrences of a phenomenon.
But sometimes you only want each value or category represented and summarized once, which means you’ll need to find and consolidate all instances of duplication. Let’s start with finding those duplicates.
Download your free practice file!
Use this free Excel file to practice along with the tutorial.
How to find duplicates
If you only want to identify duplicate values in Excel but not remove them, conditional formatting may be just the feature you’re looking for.
Depending on the type of duplicates you’d like to isolate, you may consider creating an extra column to join the entire row or range of cells into a single string.
In the following dataset, each column has a duplicate value somewhere (there are two Roberts, two Longs, four Jersey Cities, and two FLs). But our real concern is to identify rows that are true duplicates — identical in every way.

In the example below, we used the TEXTJOIN function.

- Highlight column E.
- Go to the Home tab. Click Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Duplicate Values.

- From the Duplicate Values window, with Duplicate selected in the dropdown menu, choose the format you would like to be applied to cells that are duplicated.

- Click OK.
Excel finds two pairs of duplicates and highlights them. If no further action is required, you’re good to go. But what about if you wanted to go a step further — actually removing duplicate values? To do that, you can choose from any of the methods below.
4 ways to remove duplicates in Excel
1. The Remove Duplicates command
Removing duplicates in Excel is often just three or four clicks away. The Data tab carries a Remove Duplicates icon right on the ribbon.

- Click anywhere within the dataset where you’d like Excel to delete duplicates.

- If your data has headers, ticking the “My data has headers” box in the Remove Duplicates window will ensure that your first row isn’t part of the removal process.
- Tick the columns where you want to search for and remove duplicates. Excel will evaluate each row based on data across all values in the ticked columns. Any row where the values in these columns are identical will be reduced to a single row, removing any duplications. To demonstrate this, we will tick only the First Name column.
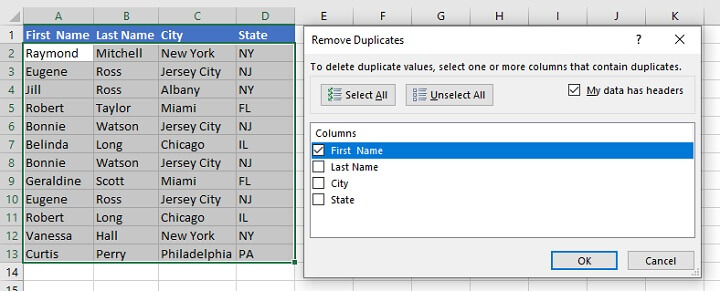
- Click OK.
Excel removed three duplicate values (Eugene, Bonnie, and Robert) and their associated rows, leaving only rows with unique first names.

2. Using advanced filters
The advanced filters feature enables you to copy the data right there on the worksheet just by clicking a button. You may want to do this to compare the “before and after” datasets side by side. Here’s how it’s done:
- Click any cell within the dataset.
- Go to the Data tab on the ribbon and click Advanced within the Sort and Filter command group. This will open up the Advanced Filter window.

- From the Advanced Filter window, selecting the Copy to another location radio button gives you the option of placing the new dataset somewhere else on the active worksheet.
- Confirm or adjust the data area by double-checking the list range.
- Since we aren’t looking to extract or filter special values, the Criteria range field should be empty.
- In the Copy to field, enter the cell reference where the new dataset will begin.
- Check the box for Unique records only.

- Press OK.
Since Eugene Ross and Bonnie Watson are duplicated, the duplicate rows are deleted and a new dataset is created beginning at cell F1.
One drawback with advanced filters is that the filter isn’t dynamic, meaning that the extracted list does not update itself if the values in your original dataset change. The filter has to be reapplied.
Another limitation is that while your advanced filter can be in a different location on the worksheet, it must be on the same worksheet as the original dataset.
3. Using pivot tables
What about using a pivot table to remove duplicates? To be clear, you won’t actually be removing duplicate values from your data with this method. You’ll be using a pivot table to display only the unique values from the data set. First, create a pivot table by doing the following:
- Select a cell inside your Excel table or the entire range of data.
- Go to the Insert tab and select PivotTable.
- Press OK in the Create PivotTable dialog box.

- Select all the fields to add to the Rows area of the table. This isn’t looking the way we expect, so we’ll need to change the format.
- Go to the Design tab. From there select Report Layout. There are two options you will need to change:
- Select - Show in Tabular Form.
- Select - Repeat All Item Labels.
- Still on the Design tab, select Subtotals and click Do Not Show Subtotals.

4. Using Power Query
Power Query has a command to remove duplicates right within the interface. Like several of our other methods, you can remove duplicates based on one or more columns in the table.
The steps are as follows:
- Go to the Data tab and from the Get & Transform Data command group, click the From Table/Range icon.
- To select multiple columns to check for duplicates, hold down the Ctrl key and click the relevant column headings.
- Right click one of the selected column headings and choose Remove Duplicates from the contextual menu.

- Click Close & Load and your original dataset is updated.

- Note that the dataset must be formatted as an Excel table to use Power Query.
Conclusion
With so many options available to remove “noisy” duplicate data, your greatest challenge will be to choose the one you’re happiest with. Download the practice file and practice the methods we used above.
Then try our free Excel crash course to get familiar with some Excel basics. Then level up your skills and become an Excel ninja with our Excel Basic and Advanced course.
Ready to become a certified Excel ninja?
Start learning for free with GoSkills courses
Start free trial




